Table of Contents
Virtualization Definition
Virtualization is the technology that simulates hardware functionality to create software-based IT services such as application servers, storage, and networking.
In practical terms, imagine we take three physical servers with individual-specific purposes. The first is a mail server, the second web server, and the third runs internal legacy applications.
Each server uses about 30% of its capacity; that is, only a part of its execution potential.
But since legacy applications are still essential to your internal operations, you have to keep them together with the third server that hosts them, right? Usually, the answer is yes.
Generally, it was more comfortable and more reliable to run individual tasks on individual servers.
A server is an operating system and a task. It was not easy to assign multiple tasks to a server.
But virtualization allows you to divide your mail server into two single servers that can handle separate tasks.
So that legacy applications can be migrated. The same hardware is used, but more efficiently.
How does Virtualization Work?
- Software called hypervisors separates physical resources from virtual environments, that is, everything that resources need.
- Hypervisors it is shaped as core elements of an operating system (like a laptop), or they can be installed directly on the hardware (like a server), which is the way most companies virtualize.
- Hypervisors take physical resources and divide them in such a way that virtual environments can use them.
- Resources are divide according to needs, from the physical environment to the many virtual environments.
- Users interact with and run calculations within the virtual environment (generally referred to as a guest machine or virtual machine).
- The virtual machine works the single data file. As with any digital file, it can be moved from one computer to another, opened in anyone, and expect it to work the same way.
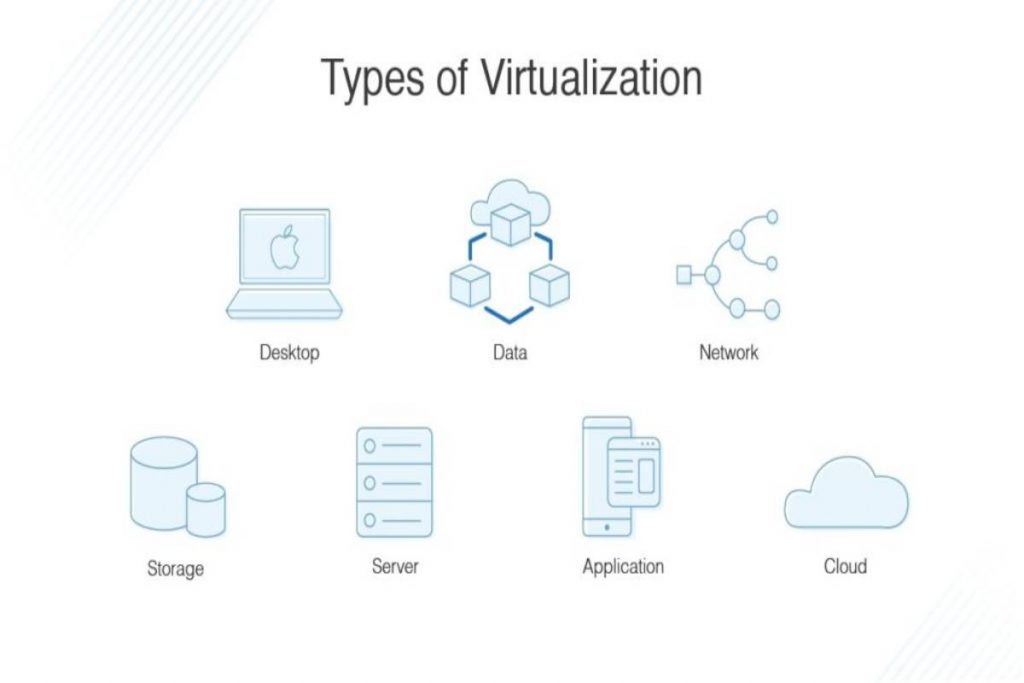
What are the Types of Virtualization?
1. Data Virtualization
- Data that scattered everywhere can joined into a single source.
- And data virtualization allows companies to treat it as a dynamic supply chain.
- In this way, you get the processing capacity that will enable you to gather data from various sources.
- Integrate other new sources with ease, and transform the data according to the needs of users.
- Data virtualization tools address multiple data sources and allow them to be reliable as one.
- It is possible to provide any application or user with the necessary data, in the required way and at the right time.
2. Desktop Virtualization
- Desktop virtualization often easily confused with operating system virtualization.
Which it is allows us to deploy multiple operating systems on a single machine. - However, with desktop virtualization, a central administrator (or an automated management tool) can deploy simulated desktop environments on hundreds of physical machines simultaneously.
3. Server Virtualization
- Servers are computers designed to process a large volume of specific tasks very effectively.
- So that other computers, such as laptops or desktops, can perform different tasks.
- Virtualizing a server allows you to perform more specific functions and involves breaking it down so that the elements can be rummage-sale to perform various functions.
What is Operating System Virtualization?
- The virtualization of the operating system is complete in the kernel, the central task managers of the operating systems.
- It’s a helpful way to run Linux and Windows environments in parallel. Companies can also embed virtual operating systems in computers, which.
- And also it reduces the cost of hardware in bulk since computers do not require such immediate capabilities.
- And also it increases security because all virtual instances can remain observed and isolated.
- Limit the time spent on IT services, such as software updates.
What is Network Functions Virtualization?
- Network functions virtualization (NFV) separates a network’s critical functions (such as directory services, file sharing, and IP configuration) to distribute them across environments.
- When software roles become independent of the virtual machines they were in, specific functions can bundled into the new network and assign to the environment.
- Network virtualization reduces the number of physical components (such as switches, routers, servers, cables, and hubs).
- That needs to create multiple independent networks and is very popular in the telecommunications industry.
Also Read: What is the Bootstrapping? – Definition, Five Ideas of bootstrapping in the business
Also Read: What is Organic Search? – Definition, Position, Factors, and More