Introduction
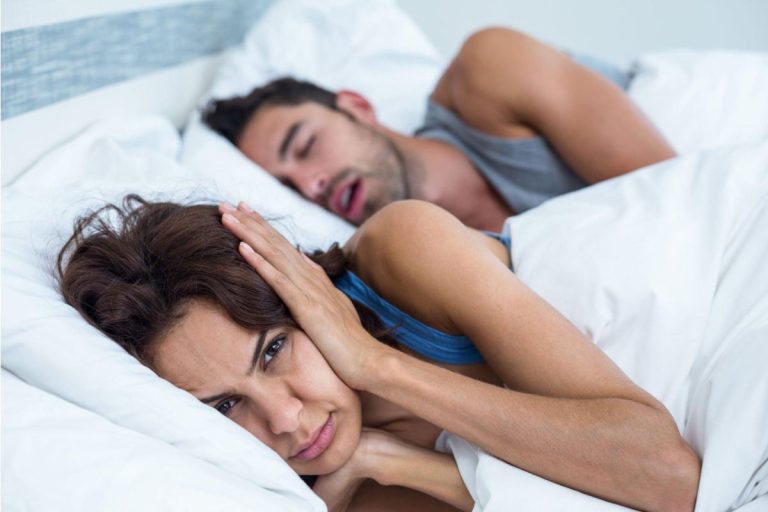
As per the wellhealthorganic.com:if-you-are-troubled-by-snoring-then-know-home-remedies-to-deal-with-snoring – Snoring can be one of the most annoying sounds that irritate your partner, your family, and even yourself. However, the excellent news is that you don’t have to put up with it anymore! You can learn how to stop snoring at home with simple tips, home remedies, and lifestyle changes.
In this guide from Wellhealthorganic.com, we’ll review everything you need to know about snoring and how to get long-term relief. From the basics of why people snore to identifying potential causes of snoring, we’ll discuss all the things that could potentially be causing your discomfort—and what steps you can take to fix them. We’ll also provide tried-and-true home remedies perfect for anyone who wants to solve their snoring problem without medication or medical intervention.
So whether you’re hoping to find relief from your snoring or looking for advice on helping your loved one find respite from their nighttime noise, this guide is here to help. Read on and get started down the path toward sleeping sounder tonight!
What Is Snoring?

As per the wellhealthorganic.com:if-you-are-troubled-by-snoring-then-know-home-remedies-to-deal-with-snoring – If you’re trouble by snoring or have heard the sound of yourself snoring—you may be wondering what it is and why it’s happening. In short, snoring occurs when the airflow from your mouth or nose vibrates the surrounding tissue. It is often cause by a blockage or partial blockage in your airway while you sleep. As we age, our throats become narrower and muscles become more relaxed, making snoring worse.
Below are a few other factors that can contribute to snoring, too, such as:
- Drinking alcohol before bed
- Taking certain medications
- Being overweight
- Having allergies
- Smoking
These can cause the narrowing of your airways, making it harder for air to move through them freely and resulting in the vibrations known as snoring. Fortunately, some remedies can help you manage the condition so you can rest peacefully through the night.
Causes and Consequences of Snoring
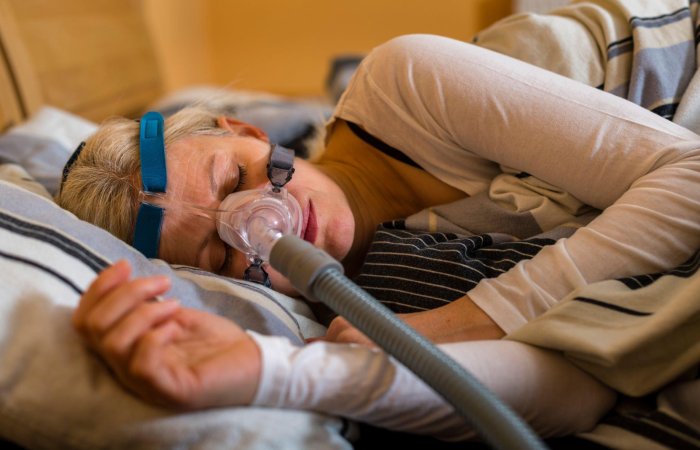
Several factors, such as nasal and sinus congestion, narrow nasal passages, poor throat muscle tone, airway obstruction, and obesity, can cause snoring. Snoring can cause disturbances in the quality of sleep, leading to feeling tired during the day and lacking mental alertness. It can also affect people around you, as it usually gets louder when sleeping on your back.
As per the wellhealthorganic.com:if-you-are-troubled-by-snoring-then-know-home-remedies-to-deal-with-snoring, specific lifestyle changes and home remedies can help reduce or manage snoring. Some helpful tips to try include:
- Elevating your head four inches while sleeping on your back may help reduce snoring.
- Losing weight if you are overweight may decrease snoring frequency by improving muscle tone in the throat.
- You are avoiding alcohol late at night because drinking alcohol relaxes your throat muscles and makes them more prone to vibrate during sleep.
- I am avoiding cigarettes and smoke, which irritates the throat muscles and causes them to become inflamed, narrowing the air passage.
- Keeping yourself hydrated as dry air can also irritate your throat, leading to snoring.
Understanding the Science of Snoring
According to the wellhealthorganic.com:if-you-have-a-problem-with-snoring-then-learn-home-remedies-to-deal-with-snoring. Snoring is a common problem that affects millions of people around the world. It occurs when airflow through the mouth and nose is partially blocked during sleep, causing the tissues in the throat to vibrate and creating a sound of Snoring.
Several factors can affect Snoring, including age, weight, alcohol consumption, smoking, and anatomical abnormalities in the nose and throat. It can also indicate a severe further condition called sleep apnea, in which breathing stops and starts repeatedly during sleep.
Snoring can significantly affect sleep quality and lead to daytime sleepiness, irritability, and difficulty concentrating. It can also increase your risk of severe health problems like high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke.
To reduce or eliminate Snoring, it is essential to understand the underlying causes. Simple lifestyle changes like weight loss, quitting smoking, and not drinking alcohol before bed can often help reduce Snoring. In more severe cases, treatments or medical devices may be needed.
How to Identify the Type of Snoring You Have
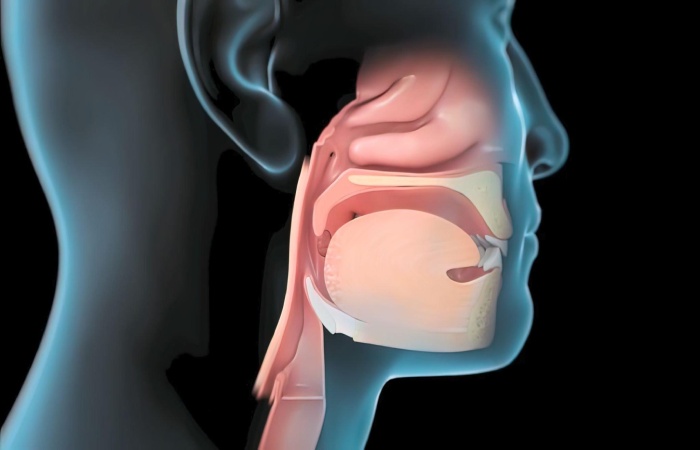
The third step in our guide is to identify your snoring type. Believe it or not, snoring can vary a lot; how severe it is and how often it happens can all affected by your snoring style, as per the wellhealthorganic.com:if-you-are-troubled-by-snoring-then-know-home-remedies-to-deal-with-snoring.
That’s why understanding the kind of snoring you’re dealing with is essential—you need to know what you’re up against before finding suitable home remedies. So let’s take a quick look at the two types of snoring:
Primary snoring
Primary or solo snoring is pretty standard and occurs when your airways are partially blocked while sleeping—causing vibration of surrounding tissue, which results in noise. If you have primary snoring, then home remedies may help reduce it.
Secondary snoring
Secondary or complicated snoring occurs when an underlying health condition blocks your airways even further, like sleep apnea, allergies, or enlarged tonsils and adenoids. The snoring is often louder, and more intense than primary snoring—so seeking medical attention is recommend if this kind of snoring persists.
Knowing what type of snoring you have will help to determine which home remedies might work best for you. In most cases (primary snoring), lifestyle changes like weight reduction and avoiding alcohol might do the trick, while secondary scorers might need treatments like mouthpieces to fight their condition.
Natural Tips for Reducing Snoring at Home
So, if you snore loudly and are looking for ways to reduce it, there are some natural tips you can try at home. These are some of the most popular ones that may help:
Change your sleeping position
Most people snore when they sleep on their back because their soft palate and tongue drop to the back of the throat and partially block the airway. Instead, consider lying on your side to reduce pressure on your airways and potentially reduce snoring.
Clear nasal passages
Nasal congestion can also cause or worsen snoring. Try taking a hot shower, using a saline nasal wash, or using a warm-mist humidifier to keep your nasal passages clear from mucus and allergens that could be causing your snoring.
Regular exercise
The good physical condition can also help in reducing snoring. Regular exercise helps build muscle tone in all areas of your body, including those in your throat, which helps keep them from relaxing so much during sleep and causing snoring.
Lose weight if needed
Excess fat around the neck can cause additional pressure on the throat muscles, narrowing the airways and leading to louder snoring. You may not even realize how much weight you’ve gained until you take off a few pounds and see (and hear) a marked reduction in the volume of your nighttime noises!
Best Home Remedies to Stop Snoring

Fortunately, there are many simple home remedies to help you stop snoring. These are some of the most actual ones you can immediately try: As per the wellhealthorganic.com:if-you-are-troubled-by-snoring-then-know-home-remedies-to-deal-with-snoring.
Positioning Pillow
Investing in a good positioning pillow is one of the quickest ways to reduce snoring. It helps to keep your body in the proper position while sleeping, which prevents the airways from getting block or restrict. Consider using one with adjustable heights to find a comfortable angle for your neck that keeps your breathing steady throughout the night.
Elevate the Head of Your Bed
Moving the head of your bed by four inches can also help reduce snoring, allowing gravity to open up your airways and making breathing more accessible for you to breathe while sleeping. If this method is uncomfortable, try putting a firm foam wedge or two pillows beneath your mattress.
Prop Up Your Body
Propping up your body with additional support, such as pillows, can also help reduce snoring. Keeping your body upright will ensure that there isn’t any extra weight on your chest. Which can cause airways to narrow and restrict breathing during sleep.
Avoid Sleeping on Your Back
Sleeping on your back can cause throat tissues and tongue muscles to relax, constricting airways and leading to snoring sounds. Avoid this position and opt for sleeping on either side instead. As it keeps the tongue from blocking airflow while you sleep.
What to Do When Natural Remedies Fail
Finally, if none of these natural remedies help you get a quieter night’s sleep. It may be time to talk to your doctors or healthcare provider. They might be able to uncover any underlying medical problems that could be contributing to your snoring. And offer solutions like dietary changes or a CPAP machine.
In some cases, lifestyle changes may not work because of physical characteristics. For example, if your airway is naturally narrow due to jaw structure. Snoring can be more challenging to address with lifestyle adjustments. If this is the case for you, consider talking with an ENT (ear nose throat). Specialist about available treatments for more severe snoring conditions.
There are plenty of options, from special pillows and chin straps to surgeries and implants. If you feel natural remedies aren’t helping enough. It would help if you considered all possibilities regarding addressing snoring and improving sleep quality.
Conclusion
As per the wellhealthorganic.com:if-you-are-troubled-by-snoring-then-know-home-remedies-to-deal-with-snoring – Making a few simple lifestyle changes can make you more restful sleep and help reduce snoring. It is essential to realize that snoring can be a symptom of obstructive sleep apnea, which requires medical attention. If home remedies do not help, make sure to consult your doctor.
At wellhealthorganic.com, we are dedicate to helping you take control of your health. Taking a few simple steps to address snoring can make all the difference in your quality of life. With the right resources, you can find the best home remedies to stop snoring and get a good night’s sleep.